The Manufacturing Process of Wire Harnesses
Leave a CommentWire harnesses consist of bundles of wire, cable, or subassemblies, combined with other conductive materials, and they are used to transmit electricity in various applications. The bundling of these components makes it easier to install electrical components for signaling or power transmission. In addition, other benefits of using wire harnesses include increased productivity, lower costs, and improved safety by minimizing trip hazards and wire damage.
What Are Wire Harnesses Used for?
A wire harness, also known as a wiring assembly or cable harness, groups multiple wires, cables, or subassemblies to supply electrical power or transmit signals in many applications.
Wire harnesses have multiple applications and uses that make them suitable for many industries. A few of the main markets that use wire harnesses include the medical, military, and industrial industries. The transportation industry also frequently uses them in automobiles, trucks, buses, and planes. Other applications include industrial equipment, construction machinery, household appliances, and electronics.
The Manufacturing Process of Wire Harnesses
The wire harness manufacturing process ranges from basic to complex, depending on the end product. While it can be challenging, time-consuming, and task-oriented, a streamlined manufacturing process helps maintain efficiency and quality with each wire harness. The following is a breakdown of the different steps of the process and what they entail:
Design
While wire harnesses often appear simple, a clear, accurate design phase is critical to setting production and the manufacturing process up for success. This stage may involve choosing harness components, specifying different colors to identify specific wires, specifying all wire and cable lengths, and various other details.
Prototyping
Following the design stage, prototyping takes place. This entails developing a physical product based on the chosen design specifications. In the process, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement and determine how to approach the rest of the manufacturing process. This helps ensure optimal quality and process performance before beginning the first production run.
Production & Assembly
During production and assembly, manufacturers must meet design specifications and make sure the end product meets quality standards with minimal risk of errors. The production process still heavily relies on manual assembly even as manufacturing becomes increasingly automated.
Throughout this stage, manufacturers typically complete three main steps:
- Wire Cutting — The first step in the production phase involves cutting wires to their designated lengths using a wire-cutting machine.
- Stripping and Connections — After cutting, the next step entails stripping the wire ends to expose their cores, which allows for the attachment of connector housings, terminals, or modules.
- Assembly — The last step is the wire harness assembly process, which involves putting together the wire harness using an assembly board or workbench to put the final product together based on design specifications.
Testing
Following the core manufacturing process, manufacturers test the end product for quality assurance purposes. If the product meets quality and performance standards, the manufacturer ships the final product to the client.
Top-Quality Wire Harnesses from Electro-Prep
Various applications require reliable wire harnesses for transmitting electricity/data. If you’re in need of a wire harness for your application, Electro-prep can manufacture custom wire harnesses based on your unique requirements.
To learn more about our wire harness manufacturing capabilities, contact us today. If you would like to get started, request a quote from us and we’ll connect you with one of our experts.
Ribbon Cables
Leave a CommentAlso called a planar cable or flat ribbon cable, a ribbon cable has a wide, flat rectangular shape that resembles a ribbon. Each ribbon cable holds parallel wires that run on a flat plane. The distinct design makes it easier to work with when space is limited. Learn more about the types of ribbon cables, their advantages, and what to consider when choosing the right cables for your application.
Types of Ribbon Cables
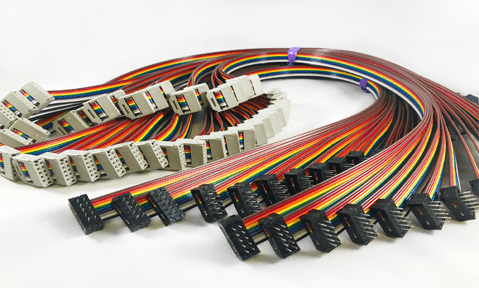 Ribbon cables are available in a few different styles and configurations. The most popular types from most common to least common are:
Ribbon cables are available in a few different styles and configurations. The most popular types from most common to least common are:
- Standard. The standard ribbon cable is identified by its gray color and is commonly used for mass termination applications.
- Rainbow. Rainbow ribbon cables are color-coded standard cables, which make organization and identification easier. In some cases, each colored ribbon is split into individual terminations.
- Round-to-flat. This type of cable starts bundled in a circular shape, then flattens into a ribbon. The round-to-flat ribbon cable is adaptable and ideal in tight spaces.
- Twisted flat. A variant of standard ribbon cables, twisted flat ribbon cables have pairs of conductors that are twisted and bonded together. They have alternating twisted and untwisted parallel sections. Distinct from twisted pair cables, a twisted flat ribbon cable has parts of the cable that are not twisted. This design allows the connectors and PCB headers to be terminated with conventional IDC ribbon cabling techniques.
- Bonded. Bonded ribbon cables lack the flexibility of other ribbon cable types, but bonded cables simplify mass termination. The bonded design better organizes the cables from one end to the other.
Considerations for Choosing Ribbon Cables
When selecting ribbon cables for your application, consider the following specifications:
- Pitch. The pitch pertains to the spacing of conductors within a ribbon cable. Common pitch measurements are 0.5 mm, 1 mm, 1.25 mm, and 2 mm. The correct pitch will vary based on various ribbon cable requirements.
- Extreme temperatures. Basic ribbon cables work just fine in moderate temperatures. For high-temperature environments, a silicon jacket may be necessary to protect the ribbon cable.
- Flexibility. A standard ribbon cable is very flexible. For settings with extremely limited space, you may need to order a customized ribbon cable with greater flexibility.
- Long life. Choose ribbon cables that have been tested and rated for longevity.
- Fire resistance. Fire resistance is important for both the safety and functionality of the electrical device. Be sure to choose a ribbon cable that is fully compliant with the fire safety regulations of its intended application.
Advantages of Standard Copper Conductor Ribbon Cables
The key advantages of ribbon cables are flexibility, customizability, space efficiency, and noise reduction. In the past, ribbon cables had limited applications due to unique termination techniques. However, modern innovations in ribbon cable technology have enabled engineers to use standard cable preparation tools and automation. Now, ribbon cables can be mass terminated by solder-cup connectors or crimp contacts and configured for a wide range of electrical applications.
Reliable Ribbon Cables From Electro-Prep
The expert team at Electro-Prep can help you design ribbon cables tailored to your project. All of our employees are trained in-house, allowing us to provide a consultative approach for every client. We can provide you with the ideal ribbon cable paired with desired specifications to match your project’s needs. Electro-Prep offers customizable options that include:
- 2 to 100 conductors in wide-spacing to high-density configurations
- MDR, IDC, and other connector options
- Integration with electronic components and materials
- Full electrical continuity testing with Cirrus test systems
- Flat flexible cable (FFC) alternatives
Contact us today to learn more about our products and capabilities.





